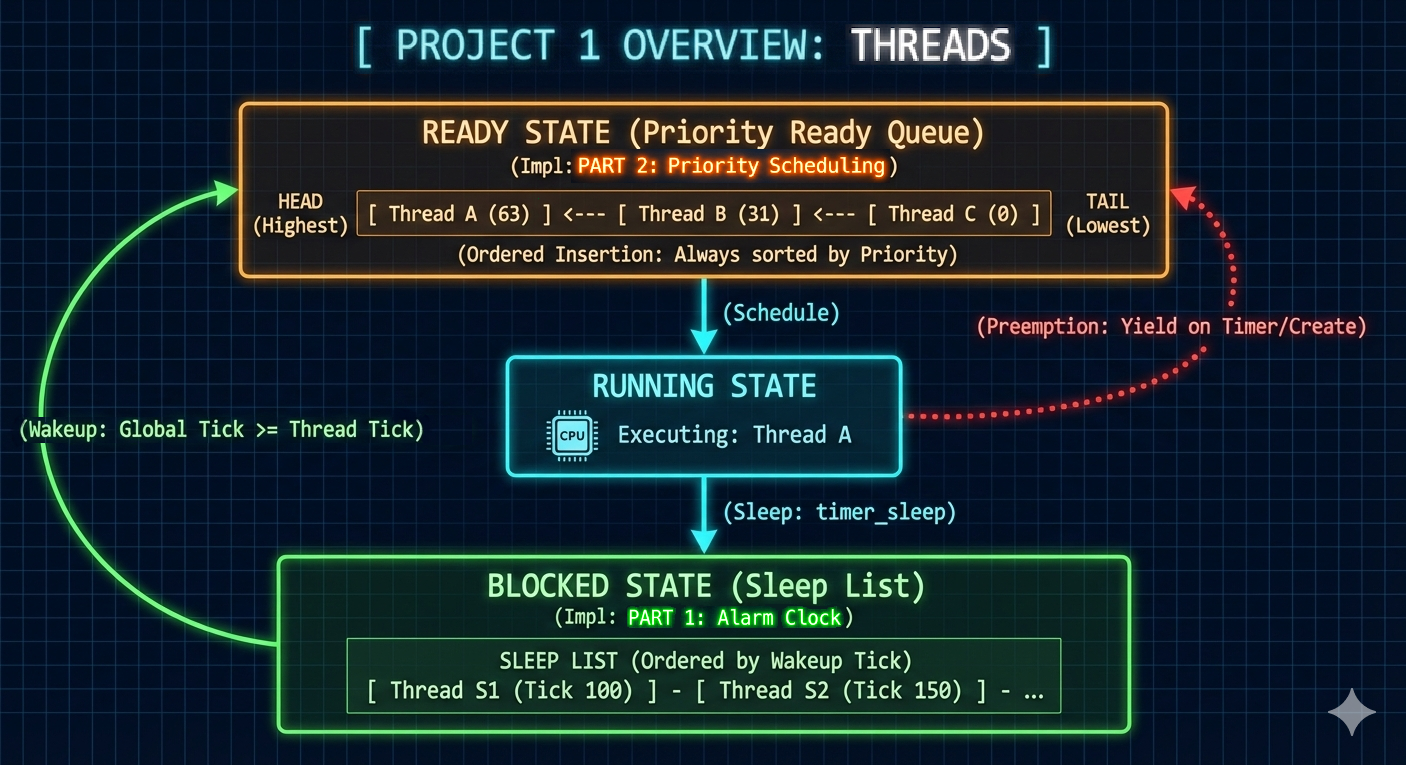
Project 1: Threads
스레드 (Threads)
- 첫 번째 프로젝트는 PintOS에 대한 두 가지 중요한 개선 사항을 포함했습니다:
- 알람 시계 메커니즘의 최적화.
- 선점 및 우선순위 기부를 통합한 우선순위 기반 스케줄링 알고리즘 구현.
-
아래에서는 각 구성 요소에 대한 목표, 도전 과제, 해결책 및 구현을 간략하게 설명했습니다.
Part 1: 알람 시계 (Alarm Clock)
목표
- 이 개선의 주요 목표는 PintOS 내의
timer_sleep()함수를 비효율적인 바쁜 대기(busy-waiting) 패러다임에서 더 효율적인 수면/깨우기 메커니즘으로 전환하여 최적화하는 것입니다. - 이 최적화는 두 가지 핵심 구성 요소를 포함합니다:
THREAD_BLOCKED상태 활용:- CPU 사이클을 능동적으로 소모하는 대신, 스레드는 잠자는 동안 블록된 상태(blocked state)로 진입하여 CPU가 다른 작업에 할당될 수 있도록 합니다.
sleep_list도입:- 재개를 기다리는 스레드를 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 전용 리스트가 사용되며, 깨어날 시간이 되었을 때 신속하게 식별하고 활성화할 수 있도록 합니다.
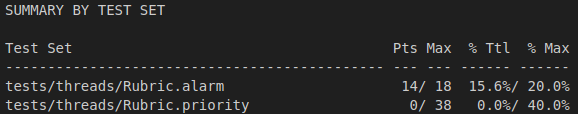
현재 문제
-
기존의
timer_sleep()시스템 호출은 바쁜 대기(busy waiting)를 사용하여 지정된 수의ticks동안 프로세스를 일시 중지합니다.Click to see the original code
timer_sleep (int64_t ticks) { int64_t start = timer_ticks (); ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_ON); while (timer_elapsed (start) < ticks) thread_yield (); } -
이 접근 방식은 몇 가지 비효율성을 보입니다:
- 반복적인 시간 확인: 촘촘한 루프 내에서 현재 시간을 반복적으로 확인합니다.
thread_yield()호출: 깨어날 시간이 아직 되지 않은 경우,thread_yield()를 호출하여 스레드를THREAD_READY상태로 전환합니다.- 결정적인 문제: 만약
ready_list에 다른 스레드가 존재하지 않는다면, 동일한 스레드가 즉시THREAD_RUNNING으로 재스케줄링됩니다.- 이는 끊임없는 양보(yielding)와 재실행(re-running)의 순환을 만들어내어 상당한 CPU 자원 낭비를 초래합니다.
원래 점수
해결책
- 위에 언급된 문제들을 해결하기 위해,
timer_sleep()함수는 다음과 같이 재구현되었습니다:- 불필요한 CPU 소모를 방지하기 위해
THREAD_BLOCKED상태를 활용하여 스레드를 일시 중단합니다. - 잠자는 모든 스레드를 효과적으로 추적하고 관리하기 위해
sleep_list데이터 구조를 도입합니다.
- 불필요한 CPU 소모를 방지하기 위해
timer_sleep()호출에 대한 수정된 워크플로우는 다음과 같습니다:- 호출 스레드는 새로운
thread_sleep()함수를 통해sleep_list에 추가됩니다. - 시스템은 주기적으로 현재 시간을 확인합니다. (예: 타이머 인터럽트 핸들러 내에서.)
- 스레드의 지정된 깨어날 시간이 되면,
thread_wakeup()함수를 통해sleep_list에서ready_list로 이동되어 스케줄링 대상이 됩니다.
- 호출 스레드는 새로운
구현 세부 사항
- 다음 구성 요소들이 수정되거나 도입되었습니다:
timer.ctimer_sleep()- 프로세스가 잠들어야 할 때
thread_yield()호출이thread_sleep()으로 대체되었습니다.Click to see the refined code
void timer_sleep(int64_t ticks) { int64_t start = timer_ticks(); ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_ON); while(timer_elapsed(start) < ticks) thread_sleep(ticks); }
- 프로세스가 잠들어야 할 때
timer_interrupt()- 현재
timer_ticks()값을 이용한thread_wakeup()호출이 추가되었습니다.Click to see the refined code
static void timer_interrupt (struct intr_frame *args UNUSED) { ticks++; thread_tick (); thread_wakeup(ticks); // wake up! }
- 현재
thread.hstruct thread- 스레드가 깨어나야 할 특정 틱(tick)을 저장하기 위해
int64_t tick_wakeup이라는 새로운 멤버가 추가되었습니다.Click to see the refined code
struct thread { // other codes struct list_elem elem; /* List element. */ int64_t tick_wakeup; /* Tick till wake up */ // other codes }
- 스레드가 깨어나야 할 특정 틱(tick)을 저장하기 위해
thread.csleep_listtimer_sleep()로 인해 현재THREAD_BLOCKED상태에 있는 스레드를 관리하기 위해 새로운 정적 리스트static struct list sleep_list가 도입되었습니다.Click to see the refined code
/* List of all processes. Processes are added to this list when they are first scheduled and removed when they exit. */ static struct list all_list; /* List of processes in THREAD_BLOCKED state. Processes are added to this list when they are called with thread_sleep() and removed when wakeup() is called */ static struct list sleep_list;
thread_init()sleep_list는 이제thread_init()함수 동안 초기화됩니다.Click to see the refined code
void thread_init (void) { ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_OFF); lock_init (&tid_lock); list_init (&ready_list); list_init (&all_list); list_init (&sleep_list); /* Set up a thread structure for the running thread. */ initial_thread = running_thread (); init_thread (initial_thread, "main", PRI_DEFAULT); initial_thread->status = THREAD_RUNNING; initial_thread->tid = allocate_tid (); }
thread_wakeup()- 이 함수는
sleep_list를 반복하여tick_wakeup시간이 도달한 스레드를ready_list로 이동시킵니다.Click to see the refined code
/* Wakes up sleeping threads by checking the sleep_list and comparing its elements to the global ticks, then activates the appropriate threads. */ void thread_wakeup(int64_t current_ticks) { enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable(); struct list_elem *current_element = list_begin(&sleep_list), *next_element = NULL; while (current_element != list_end(&sleep_list)) { struct thread *thread_to_check = list_entry(current_element, struct thread, elem); next_element = list_next(current_element); if (thread_to_check->tick_wakeup <= current_ticks) { list_remove(current_element); thread_unblock(thread_to_check); // put this thread to ready_list } current_element = next_element; } intr_set_level(old_level); }
- 이 함수는
thread_sleep()- 이 함수는 호출하는 스레드의 상태를
THREAD_BLOCKED로 설정하고, 깨어날 시간(tick_wakeup)을 기록하며,sleep_list에 추가합니다. - 그런 다음, CPU 제어권을 양보하기 위해
thread_block()을 호출합니다.Click to see the refined code
/* Sleeps for ticks. If the current thread is not the idle thread, this changes the status of the calling thread to THREAD_BLOCKED, stores the local tick for waking up, updates the global tick if necessary, and calls schedule(). */ void thread_sleep(int64_t ticks_to_sleep) { struct thread *cur = thread_current(); ASSERT (!intr_context()); enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable(); int current_ticks = timer_ticks(); if (cur != idle_thread) { cur->tick_wakeup = current_ticks + ticks_to_sleep; list_push_back(&sleep_list, &cur->elem); } thread_block(); intr_set_level (old_level); }
- 이 함수는 호출하는 스레드의 상태를
결론
- 이 수정은
timer_sleep()에서 비효율적인 바쁜 대기 메커니즘을 성공적으로 제거하여, 스레드가 잠자는 동안 CPU가 다른 작업을 수행할 수 있도록 함으로써 PintOS 내에서 CPU 효율성을 크게 향상시킵니다.
Part 2: 우선순위 (Priority)
목표
- 이 섹션의 주요 목표는 PintOS의 스케줄링 메커니즘을 근본적으로 변환하는 것입니다.
- 여기에는 기존의 FIFO 스케줄링을 강력한 우선순위 기반 시스템으로 대체하고, 고우선순위 스레드가 즉각적이고 효과적으로 실행되도록 선점(preemption)을 통합하는 것이 포함됩니다.
현재 문제
- FIFO 스케줄링
- 원래 PintOS 설계는 엄격한 FIFO (선입선출) 스케줄링 정책을 사용합니다.
-
스레드는 할당된 우선순위와 완전히 무관하게 도착한 순서대로
ready_list에 추가됩니다.Click to see the original code
void thread_unblock (struct thread *t) { enum intr_level old_level; ASSERT (is_thread (t)); old_level = intr_disable (); ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED); list_push_back (&ready_list, &t->elem); t->status = THREAD_READY; intr_set_level (old_level); }
- 선점 부재 (No Preemption)
- 현재 시스템의 중대한 한계는 선점(preemption)이 없다는 것입니다.
- 고우선순위 스레드가 준비 상태가 되더라도(예: 수면 상태에서 깨어나거나 블록 해제), 저우선순위 스레드가 현재 실행 중인 경우 즉시 CPU 시간을 부여받지 못합니다.
- 이는 비효율적인 자원 활용으로 이어지며, 시간 민감도가 높은 작업에 치명적인 지연을 유발할 수 있습니다.
해결책
- 아래에 제안된 해결책은 이러한 문제들을 해결합니다:
- 생성/블록 해제 (Creation/Unblocking):
- 우선순위 비교: 새 스레드가 생성되거나 기존 스레드가 블록 해제될 때, 해당 스레드의 우선순위가 현재 실행 중인 스레드의 우선순위와 비교됩니다. 새/블록 해제된 스레드가 더 높은 우선순위를 가지면, 문맥 교환(context switch)을 유발하기 위해
thread_yield()가 호출됩니다. - 우선순위 정렬 삽입: 스레드는 더 이상 단순히
ready_list의 맨 뒤에 추가되지 않습니다. 대신, 우선순위에 따라 정렬된 순서로ready_list에 삽입되어, 항상 가장 높은 우선순위를 가진 준비 상태 스레드가 맨 앞에 있도록 보장합니다.
- 우선순위 비교: 새 스레드가 생성되거나 기존 스레드가 블록 해제될 때, 해당 스레드의 우선순위가 현재 실행 중인 스레드의 우선순위와 비교됩니다. 새/블록 해제된 스레드가 더 높은 우선순위를 가지면, 문맥 교환(context switch)을 유발하기 위해
- 추상화 수준 (Level of Abstraction):
- 낮은 추상화 수준:
thread_unblock()함수는 저수준 함수입니다. 따라서 스레드를 우선순위에 따라ready_list에 삽입하는 역할만을 전적으로 처리하도록 수정되었습니다. - 높은 추상화 수준:
thread_create()(새 스레드가 생성될 때) 또는thread_wakeup()(잠자던 스레드가 준비 상태가 될 때)와 같이 더 높은 추상화 수준을 가진 함수들이 선점(preemption)이 필요한지 평가하고, 더 높은 우선순위의 스레드가 준비 상태가 되었다면 그에 따라thread_yield()를 호출하는 책임을 집니다.
- 낮은 추상화 수준:
- 타이머 선점 (Timer Preemption):
- 타이머 인터럽트 동안 우선순위 기반 스케줄링을 강제하기 위해,
thread_yield()를 직접 호출하는 대신intr_yield_on_return()이 활용됩니다. 이 메커니즘은 인터럽트 핸들러가 인터럽트에서 복귀할 때 문맥 교환을 수행하도록 신호를 보내, 사용 가능한 경우 더 높은 우선순위의 스레드가 스케줄링되도록 합니다.
- 타이머 인터럽트 동안 우선순위 기반 스케줄링을 강제하기 위해,
- 우선순위 기부 (Priority Donation):
- 우선순위 역전(priority inversion) 문제(고우선순위 스레드가 저우선순위 스레드가 보유한 리소스를 기다리느라 블록되는 문제)를 완화하기 위해,
struct thread에 추가 필드(donors와lock_to_wait)가 추가됩니다. 이는 저우선순위 스레드가 자신이 보유한 락 때문에 블록된 고우선순위 스레드의 우선순위를 일시적으로 상속받는 메커니즘을 가능하게 합니다.
- 우선순위 역전(priority inversion) 문제(고우선순위 스레드가 저우선순위 스레드가 보유한 리소스를 기다리느라 블록되는 문제)를 완화하기 위해,

- 생성/블록 해제 (Creation/Unblocking):
구현 세부 사항
- 다음 구성 요소들이 수정되거나 도입되었습니다:
thread.hstruct thread- 우선순위 기부 및 추적을 용이하게 하기 위해 새로운 멤버
lock_to_wait,original_priority,donors, 그리고donelem이 추가되었습니다.Click to see the refined code
struct thread { // other codes int64_t tick_wakeup; /* Tick till wake up */ struct lock *lock_to_wait; /* Address of the lock to wait */ int original_priority; /* Original Priority value */ struct list donors; /* Doners for priority inversion */ struct list_elem donelem; /* List element for donors list */ // other codes };
- 우선순위 기부 및 추적을 용이하게 하기 위해 새로운 멤버
thread.cinit_thread()- 새로운 필드
wait_to_lock,original_priority, 그리고donors가 각 새 스레드에 대해 초기화됩니다.Click to see the refined code
static void init_thread (struct thread *t, const char *name, int priority) { enum intr_level old_level; ASSERT (t != NULL); ASSERT (PRI_MIN <= priority && priority <= PRI_MAX); ASSERT (name != NULL); memset (t, 0, sizeof *t); t->status = THREAD_BLOCKED; strlcpy (t->name, name, sizeof t->name); t->stack = (uint8_t *) t + PGSIZE; t->priority = priority; t->magic = THREAD_MAGIC; t->lock_to_wait = NULL; t->original_priority = priority; list_init(&t->donors); old_level = intr_disable (); list_push_back (&all_list, &t->allelem); intr_set_level (old_level); }
- 새로운 필드
thread_sleep()- 스레드는 이제 더 빠른 깨어날 시간과 더 높은 우선순위를 가진 스레드를 우선하도록 정렬된 방식으로
sleep_list에 삽입됩니다.Click to see the refined code
void thread_sleep(int64_t ticks_to_sleep) { struct thread *cur = thread_current(); ASSERT (!intr_context()); enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable(); int current_ticks = timer_ticks(); if (cur != idle_thread) { cur->tick_wakeup = current_ticks + ticks_to_sleep; struct list_elem *current_element = list_begin(&sleep_list); while (current_element != list_end(&sleep_list)) { struct thread *thread_current_element = list_entry(current_element, struct thread, elem); if (thread_current_element->priority < cur->priority || ((thread_current_element->priority == cur->priority) && (thread_current_element->tick_wakeup > cur->tick_wakeup))) break; current_element = list_next(current_element); } list_insert(current_element, &cur->elem); } thread_block(); intr_set_level (old_level); }
- 스레드는 이제 더 빠른 깨어날 시간과 더 높은 우선순위를 가진 스레드를 우선하도록 정렬된 방식으로
thread_wakeup()- 이 함수는 이제 깨어날 틱과 우선순위를 모두 기반으로 스레드를 블록 해제하며, 선점 기회를 능동적으로 확인합니다.
Click to see the refined code
void thread_wakeup(int64_t current_ticks) { enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable(); struct list_elem *current_element = list_begin(&sleep_list), *next_element = NULL; while (current_element != list_end(&sleep_list)) { struct thread *thread_to_check = list_entry(current_element, struct thread, elem); next_element = list_next(current_element); if (thread_to_check->tick_wakeup <= current_ticks) { list_remove(current_element); thread_unblock(thread_to_check); // put this thread to ready_list } current_element = next_element; } intr_set_level(old_level); }
- 이 함수는 이제 깨어날 틱과 우선순위를 모두 기반으로 스레드를 블록 해제하며, 선점 기회를 능동적으로 확인합니다.
thread_yield()- 현재 스레드를
ready_list에 다시 삽입하는 로직이 해당 스레드의 우선순위에 따라 배치되도록 수정되어, 리스트의 정렬된 순서를 유지하도록 했습니다.Click to see the refined code
void thread_yield (void) { struct thread *cur = thread_current (); enum intr_level old_level; ASSERT (!intr_context ()); old_level = intr_disable (); if (cur != idle_thread) { bool is_inserted = false; for(struct list_elem *current_element = list_begin(&ready_list), *end_element = list_end(&ready_list); current_element != end_element; current_element = list_next(current_element)) { struct thread *thread_current_element = list_entry(current_element, struct thread, elem); if (thread_current_element->priority < cur->priority) { list_insert(current_element, &cur->elem); is_inserted = true; break; } } if(is_inserted == false) list_push_back(&ready_list, &cur->elem); } cur->status = THREAD_READY; schedule (); intr_set_level (old_level); }
- 현재 스레드를
thread_set_priority()- 이 함수는 스레드의 우선순위를 설정할 뿐만 아니라, 우선순위 기부를 관리하는 로직을 통합하고, 새로운 우선순위가
ready_list맨 앞에 있는 현재 실행 중인 스레드의 우선순위보다 높다면 선점을 유발합니다.Click to see the refined code
void thread_set_priority (int new_priority) { struct thread* current_thread = thread_current(); if(list_empty(¤t_thread->donors)) current_thread->priority = new_priority; else { if(current_thread->priority < new_priority) current_thread->priority = new_priority; } current_thread->original_priority = new_priority; if(list_empty(&ready_list) == false && current_thread->priority < list_entry(list_front(&ready_list), struct thread, elem)->priority) thread_yield(); }
- 이 함수는 스레드의 우선순위를 설정할 뿐만 아니라, 우선순위 기부를 관리하는 로직을 통합하고, 새로운 우선순위가
thread_unblock()- 이 함수는 이제 블록 해제된 스레드를 단순히 추가하는 대신 올바른 우선순위 순서로
ready_list에 삽입합니다.Click to see the refined code
void thread_unblock (struct thread *t) { enum intr_level old_level; ASSERT (is_thread (t)); old_level = intr_disable (); ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED); bool is_inserted = false; for(struct list_elem *current_element = list_begin(&ready_list), *end_element = list_end(&ready_list); current_element != end_element; current_element = list_next(current_element)) { struct thread *thread_current_element = list_entry(current_element, struct thread, elem); if (thread_current_element->priority < t->priority) { list_insert(current_element, &t->elem); is_inserted = true; break; } } if(is_inserted == false) list_push_back(&ready_list, &t->elem); t->status = THREAD_READY; intr_set_level (old_level); }
- 이 함수는 이제 블록 해제된 스레드를 단순히 추가하는 대신 올바른 우선순위 순서로
thread_create()- 새 스레드가 생성되고 블록 해제된 후, 이 함수에는 이제 새로 생성된 스레드가 현재 실행 중인 스레드보다 더 높은 우선순위를 갖는지 확인하는 검사가 포함됩니다.
- 만약 그렇다면, 즉각적인 선점을 허용하기 위해
thread_yield()를 유발합니다.Click to see the refined code
tid_t thread_create (const char *name, int priority, thread_func *function, void *aux) { struct thread *t; struct kernel_thread_frame *kf; struct switch_entry_frame *ef; struct switch_threads_frame *sf; tid_t tid; ASSERT (function != NULL); /* Allocate thread. */ t = palloc_get_page (PAL_ZERO); if (t == NULL) return TID_ERROR; /* Initialize thread. */ init_thread (t, name, priority); tid = t->tid = allocate_tid (); /* Stack frame for kernel_thread(). */ kf = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *kf); kf->eip = NULL; kf->function = function; kf->aux = aux; /* Stack frame for switch_entry(). */ ef = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *ef); ef->eip = (void (*) (void)) kernel_thread; /* Stack frame for switch_threads(). */ sf = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *sf); sf->eip = switch_entry; sf->ebp = 0; /* Add to run queue. */ thread_unblock(t); // now preform preemption if needed if(t->priority > thread_current()->priority) thread_yield(); return tid; }
synch.csemaphore_elem- 세마포어에서의 우선순위 기반 대기를 가능하게 하기 위해
struct semaphore_elem에priority필드가 추가되었습니다.Click to see the refined code
/* One semaphore in a list. */ struct semaphore_elem { struct list_elem elem; /* List element. */ struct semaphore semaphore; /* This semaphore. */ int priority /* Priority for scheduling*/ };
- 세마포어에서의 우선순위 기반 대기를 가능하게 하기 위해
sema_down()sema_down()은 수정되지 않았다는 점에 주목해야 합니다. * 이는sema_up()이 호출될 때 우선순위가 중요해지기 때문입니다.
sema_up()- 이 함수는 이제 가장 높은 우선순위의 스레드를 블록 해제하기 전에
priority를 기반으로waiters리스트를 정렬합니다.- 또한, 블록 해제된 스레드가 현재 실행 중인 스레드보다 더 높은 우선순위를 갖는 경우 선점(preemption)을 수행합니다.
Click to see the refined code
void bool compare_priority_for_waiters(const struct list_elem *lhs, const struct list_elem *rhs, void *aux UNUSED) { struct thread *thread_left = list_entry(lhs, struct thread, elem), *thread_right = list_entry(rhs, struct thread, elem); return thread_left->priority > thread_right->priority; } void sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) { enum intr_level old_level; ASSERT (sema != NULL); old_level = intr_disable (); struct thread *thread_to_unblock = NULL; if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters)) { // sort list list_sort(&sema->waiters, compare_priority_for_waiters, NULL); thread_to_unblock = list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters), struct thread, elem); thread_unblock(thread_to_unblock); } sema->value++; if(!intr_context() && thread_to_unblock != NULL && thread_to_unblock->priority > thread_current()->priority) thread_yield(); intr_set_level (old_level); }
- 이 함수는 이제 가장 높은 우선순위의 스레드를 블록 해제하기 전에
lock_acquire()- 이 함수는 이제 우선순위 기부 메커니즘을 통합합니다.
- 스레드가 잠긴 리소스를 획득하려고 시도할 때,
- 만약 보유 스레드의 우선순위가 더 낮다면, 우선순위 역전을 방지하기 위해 보유 스레드는 획득하려는 스레드의 우선순위를 일시적으로 상속받습니다.
- 또한 현재 스레드가 기다리는 락을 추적합니다.
Click to see the refined code
void lock_acquire (struct lock *lock) { ASSERT (lock != NULL); ASSERT (!intr_context ()); ASSERT (!lock_held_by_current_thread (lock)); struct thread *current_thread = thread_current(); if(lock->holder != NULL) { for(struct lock *current_lock = lock; current_lock != NULL && current_lock->holder->priority < current_thread->priority; current_lock = current_lock->holder->lock_to_wait) current_lock->holder->priority = current_thread->priority; if(lock->holder->original_priority < current_thread->priority) list_push_back(&lock->holder->donors, ¤t_thread->donelem); } current_thread->lock_to_wait = lock; sema_down (&lock->semaphore); lock->holder = current_thread; current_thread->lock_to_wait = NULL; }
lock_release()- 락을 해제할 때, 이 함수는 우선순위 기부자 목록 관리를 처리하고, 활성 상태인 더 높은 우선순위 기부가 없다면 락 보유자의 원래 우선순위를 복원합니다.
- 또한, 다중 우선순위 기부와 관련된 시나리오를 올바르게 처리합니다.
Click to see the refined code
void lock_release (struct lock *lock) { ASSERT (lock != NULL); ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock)); bool is_donor_gone = false; struct thread *thread_current_element = NULL; for(struct list_elem *current_element = list_begin(&lock->holder->donors), *end_element = list_end(&lock->holder->donors); current_element != end_element;) { thread_current_element = list_entry(current_element, struct thread, donelem); // handles multiple donation if (thread_current_element->lock_to_wait == lock) { current_element = list_remove(current_element); is_donor_gone = true; } else current_element = list_next(current_element); } struct thread *current_thread = thread_current(); if(is_donor_gone == true) current_thread->priority = current_thread->original_priority; for(struct list_elem *current_element = list_begin(&lock->holder->donors), *end_element = list_end(&lock->holder->donors); current_element != end_element; current_element = list_next(current_element)) { thread_current_element = list_entry(current_element, struct thread, donelem); if (thread_current_element->priority > current_thread->priority) current_thread->priority = thread_current_element->priority; } lock->holder = NULL; sema_up (&lock->semaphore); }
- 락을 해제할 때, 이 함수는 우선순위 기부자 목록 관리를 처리하고, 활성 상태인 더 높은 우선순위 기부가 없다면 락 보유자의 원래 우선순위를 복원합니다.
cond_wait()- 조건(condition)에 대한
waiters리스트는 이제 우선순위 순서로 유지되어, 가장 높은 우선순위를 가진 대기 중인 스레드가 먼저 신호를 받도록 보장합니다.Click to see the refined code
void cond_wait (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock) { struct semaphore_elem waiter; ASSERT (cond != NULL); ASSERT (lock != NULL); ASSERT (!intr_context ()); ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock)); sema_init (&waiter.semaphore, 0); waiter.priority = lock->holder->priority; bool is_inserted = false; for(struct list_elem *current_element = list_begin(&cond->waiters), *end_element = list_end(&cond->waiters); current_element != end_element; current_element = list_next(current_element)) { struct semaphore_elem *semaphore_current_element = list_entry(current_element, struct semaphore_elem, elem); if (semaphore_current_element->priority < waiter.priority) { list_insert(current_element, &waiter.elem); is_inserted = true; break; } } if(is_inserted == false) list_push_back(&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem); lock_release (lock); sema_down (&waiter.semaphore); lock_acquire (lock); }
- 조건(condition)에 대한
결론
- 이 포괄적인 개선은 PintOS에 우선순위 스케줄링, 선점, 그리고 견고한 우선순위 기부(priority donation) 메커니즘을 성공적으로 도입합니다.
- 이러한 변경 사항은 고우선순위 작업이 시의적절하게 실행되도록 보장하고 우선순위 역전(priority inversion)으로 인한 문제에 효과적으로 대처함으로써 운영체제의 반응성과 효율성을 크게 향상시킵니다.
향상된 점수
최종 의견
- 이러한 개선 사항들은 종합적으로 PintOS를 더욱 견고하고 효율적인 운영체제로 근본적으로 변화시킵니다.
- 지능적인 스레드 관리를 통한 자원 활용 최적화와 핵심 작업에 대한 우선순위 부여를 통해, PintOS는 이제 향상된 반응성과 전반적인 성능을 제공합니다.
Leave a comment